This lab has three experiments. We could text the Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem Activity by those 3 experiments.
Expt 1 : Work done by a nonconstant spring force.
For this experiment, we will measure the work done when we stretch a spring through a measured distance.
consider a cart being pulled by a horizontal force along a horizontal surface:
for a nonconstant force, sketch a graph of F vs. X.
then we will be able to calculate the work done by finding the area under this graph.
First,
after we did the experiment file by following steps, we got the graph of Force vs, Distance:
then we liner fit the graph, we have a slope A = 1.842 +-0.0109 which equals to the constant K of our spring. In addition. we integral this graph between 0.06m and 0.2m I = 0.03382 m*N which equals the area between 0.06m and 0.2m.
otherwise, By the work done formula:
the work done U(x) that we calculated almost equals to the area of Force vs. Distance graph between 0.06m and 0.2m.
Expt 2 : Kinetic Energy And The Work-Kinetic Energy Principle.
We were using the same set up as the experiment 1.
we measured the mass of the cart m= 0.573 kg.
For this expt, we need to use the New calculated column to calculate the kinetic energy of the cart at any point : KE(J) = 1/2 * m * v^2
Make sure that the x-axis of our graph is position, and Zero the force probe with the spring hanging loosely. Then pull the cart along the track so that the spring is stretched about 1 m from the unsretched position as same as the expt 1. we will get the graph like:
After we did this experiment by following steps, and we putted the Force vs. Position graph and KE vs. Position graph into the together, we got the graph:
the purple line means Force vs, Position. the black line means KE vs, Position.
we got the work done I= 0.07395 m*N by finding the area under the curve using the integration routine between position 0.241m and 0.3m.
And we got the change in kinetic energy of the cart after it is released from the initial position to the position 0.241m by using the analysis feature of the software. the kinetic energy = 0.074J
For the conclusions, the work done I= 0.07395 on the cart by the spring equals to its change in the kinetic energy= 0.074.
Expt 3 : Work-KE theorem.
On the Professor's computer, we watched the movie Work KE theorem cart and machine for Phys 1.mp4. In the video, the professor uses a machine to pull back on a large rubber band. The force being exerted on the rubber band is recorded by an analog force transducer onto a graph.
At the move, make a careful sketch the force vs. position graph like the picture:
Use the data, we calculated the total area A(total) = 26.595 J.
Use the formula, we calculated the final KE = 23.89 J.
Conclusion:
For this experiment, the A(total) should be very close to the KE, however, there are not very close. I think there are some reasons: the lines are not straight at all from the video, our graph may have small difference from the video,


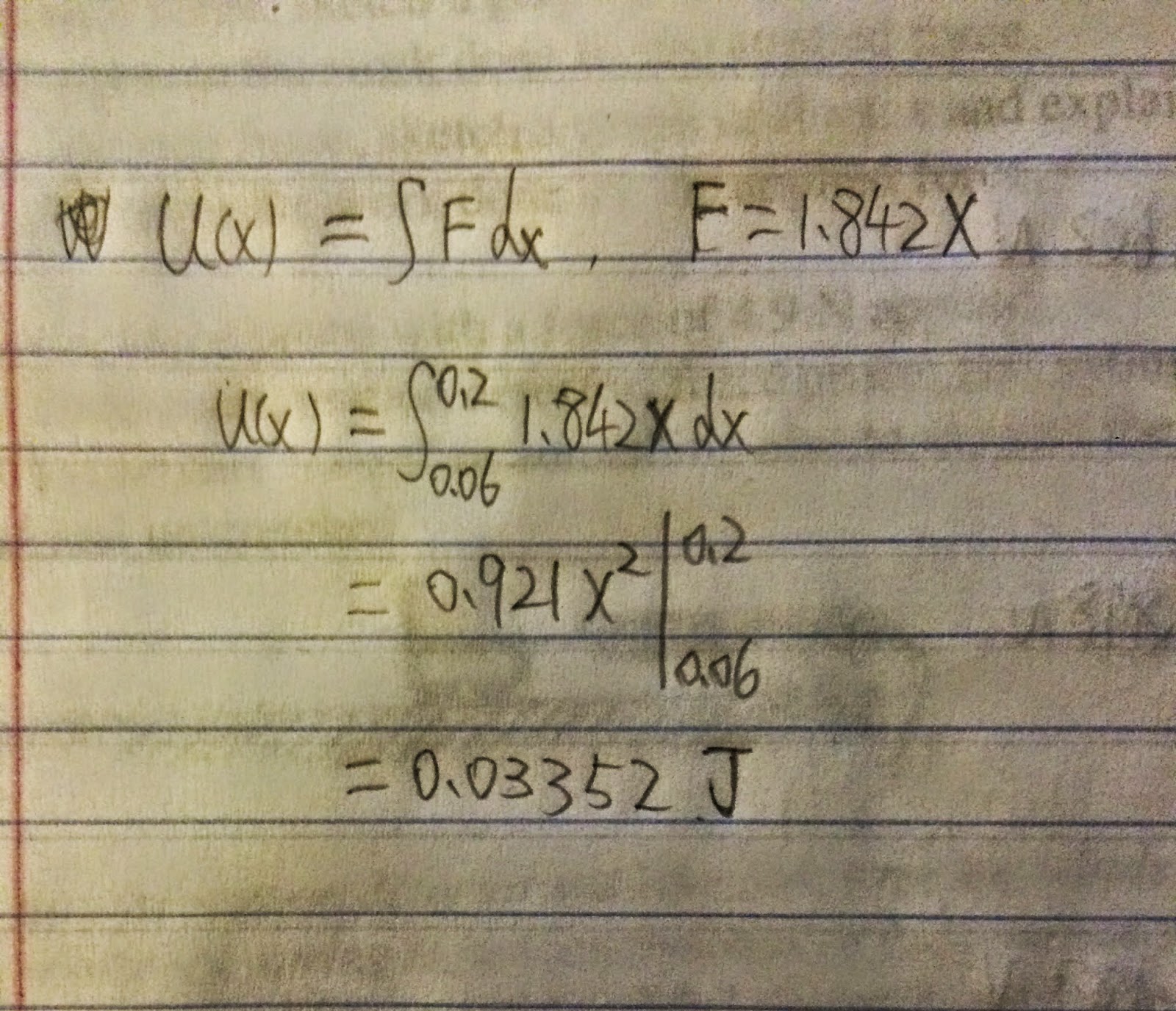



No comments:
Post a Comment